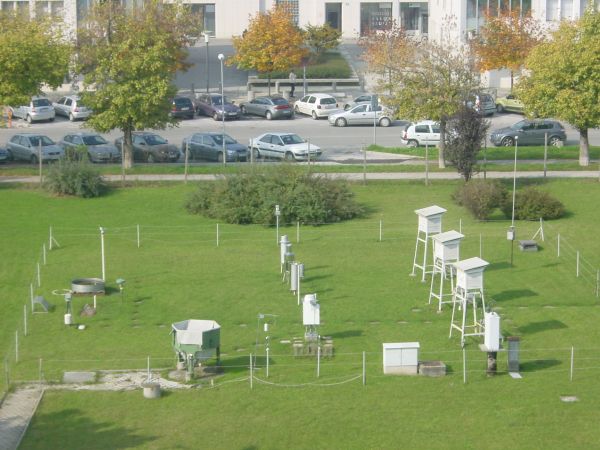

Example of observation site on the meteorological station of Ljubljana-Bežigrad
Meteorological Service is legally responsible for the implementation and
maintenance of meteorological measurements in the Republic of Slovenia.
This includes the state network of stations, which carry out the
measurements and observations of weather, and must therefore meet certain standards.
Thus data comparison is possible from different stations in Slovenia and also with data from other countries.
There are several different types of stations:
Precipitation station: observer takes measurements once per day at 7 h (CET) and measures precipitation amount, total snow depth and new snow depth. Throughout the day observer also observes 13 different atmospheric phenomena: type of precipitation (rain, hail, snow, ...) and phenomena such as fog, frost, dew, stormy winds, storm,etc.. Measurements and observations are recorded in the report and monthly sent to the Office of Meteorology.
Climatological station: observer performs measurement and observation three times a day.
At 7 h, 14 h and 21 h (CET) are recorded values of: air temperature, wind speed and direction, relative humidity, visibility, cloud, soil condition, etc..
At 7 h (CET) are measured the daily precipitation sum, total snow depth and new snow depth. At 21 h maximum and minimum day temperature has to be read from the maximum and minimum thermometer.
Throughout the day observer also observes the 45 different atmospheric phenomena.
Some stations few times a day send synop code. These encrypted reports hold measurements and observations information
and are sent to the international exchange. Measurements and observations are recorded in the report and monthly sent to the Office of Meteorology.
Synoptic meteorological station:
Measurements and observations are similar to the climatological station with more frequent observation.
The frequency of observations depends on the importance of the station.
For example at the airports ongoing observation takes place 24 hours a day.
Some stations measure also air pressure with classical mercury barometer, the temperature of the soil, water amount in snow,
the temperature of the sea, the duration of solar radiation, evaporation, etc..
All main stations send synop code to the international exchange.
Measurements and observations are recorded in the report and monthly sent to the Office of Meteorology.
Automatic weather stations: stations without observers. Measurements are made automatically. List of measurements is mainly the same as in the classical stations. Many of the automatic stations have additional sensors, for example, to measure the solar energy radiation, visibility, present weather, cloud height, etc. .. However there are limits to the observations of phenomena such as snow depth, soil condition, cloudiness, etc. because automatic stations are unable to properly record these events. Due to the effects of weather and severe weather automatic station are often disabled (struck by lightning, stormy winds, floods, avalanches, sleet, high snow, etc.), thus data from these stations can be less reliable. The advantages of automatic stations are particularly rapid access and greater temporal density of measurements (data are available once per 10 minutes or once per 30 minutes, with 5 minute sampling).
Irrespective of the station type the place of observation must be representative of their surroundings. Observed and measured values of meteorological phenomena and the elements must represent the weather and over a longer period of time also climate for the wider environs. The space in the vicinity of the location must be in the open space so that air is free to move. It is also important that in the immediate vicinity there aren't objects and buildings which can influence on measurements on the meteorological station. Measurements are performed over the maintained grass surface.

| AIR TEMPERATURE
Air temperature is measured with a mercury thermometer 2 m above the ground in white Stevenson screen. The temperature is measured in degrees Celsius (°C). Special thermometers are used to measure minimum and maximum air temperature in a single day. Air temperature is also measured 5 cm above the ground. |
 Thermometer in Stevenson screen. Thermometer in Stevenson screen. |
| AIR PRESSURE Measured by the mercury barometer. It has a glass tube, closed at one end, with an open mercury-filled reservoir at the base. Weight of column of mercury offset the weight of air. In meteorology we use the unit hektopascal (hPa). To facilitate comparison of air pressure between stations we have to calculate air pressure on the reference level, usually at the sea level. |
 Mercury barometer |
| RELATIVE HUMIDITY Relative humidity is calculated from data measured with psychrometers which consist two thermometers, one with a dry bulb and the other with a wet bulb. Evaporation from the wet bulb lowers the temperature, so that the wet-bulb thermometer usually shows a lower temperature than that of the dry-bulb thermometer, which measures dry-bulb temperature. Evaporation from the wet thermometer is larger when humidity is lower and thus difference in temperature between thermometers is larger. If the air is saturated with water vapor, both thermometers show the same temperature. When the air temperature is below 0°C it is possible that the wet thermometer shows up to 0.3 °C higher temperature than dry thermometer. On the basis of measured temperatures relative humidity can be read from the tables. |
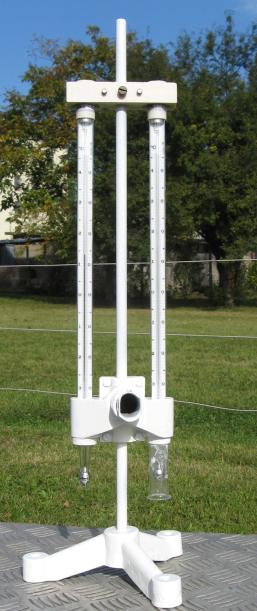 Psychrometer |
| WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION Wind speed is measured with anemometer and is measured in meters per second (m/s). It is consisted of four hemispherical cups, each mounted on one end of four horizontal arms, which in turn were mounted at equal angles to each other on a vertical shaft. Due to the unequal resistance to concave and convex side of the ball, there is a torque on the cross and the cross begins to turn: higher wind speeds means faster rotation. Wind direction is measured with wind vane. Wind direction is the direction from which a wind originates. |
 Anemometer and wind vane placed on wind tower |
| PRECIPITATION SUM Precipitation sum is measured with a measuring container, called rain gauge, ombrometer or pluviometer. Measuring container in which precipitation is collected has a precisely known dimension of interception plot. Precipitation amount is measured in liter per square meter (l/m2) or in millimeters (mm). Numeric expressions are identical with each other: if you pour 1 liter of water per square meter, water covers the floor at one millimeter thick. |
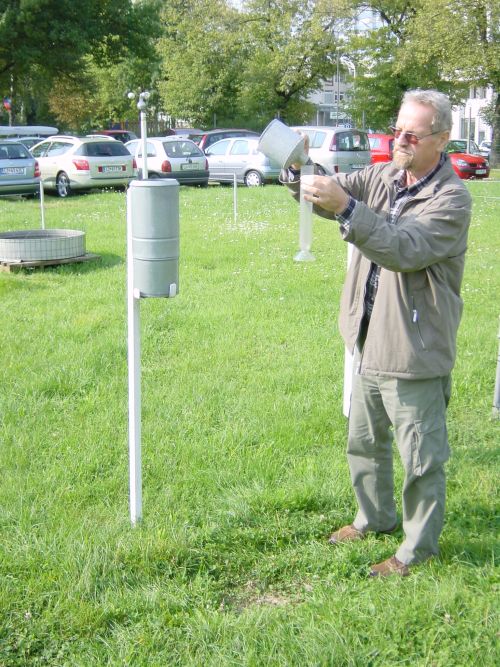 Precipitation measurements with rain gauge |
| SNOW DEPTH Depth of new snow and total snow is measured with ruler in centimeters. These are permanently installed or movable bars labeled with the scale. At the measuring site are usually more rulers. The snow depth is calculated as average of all measurements. |
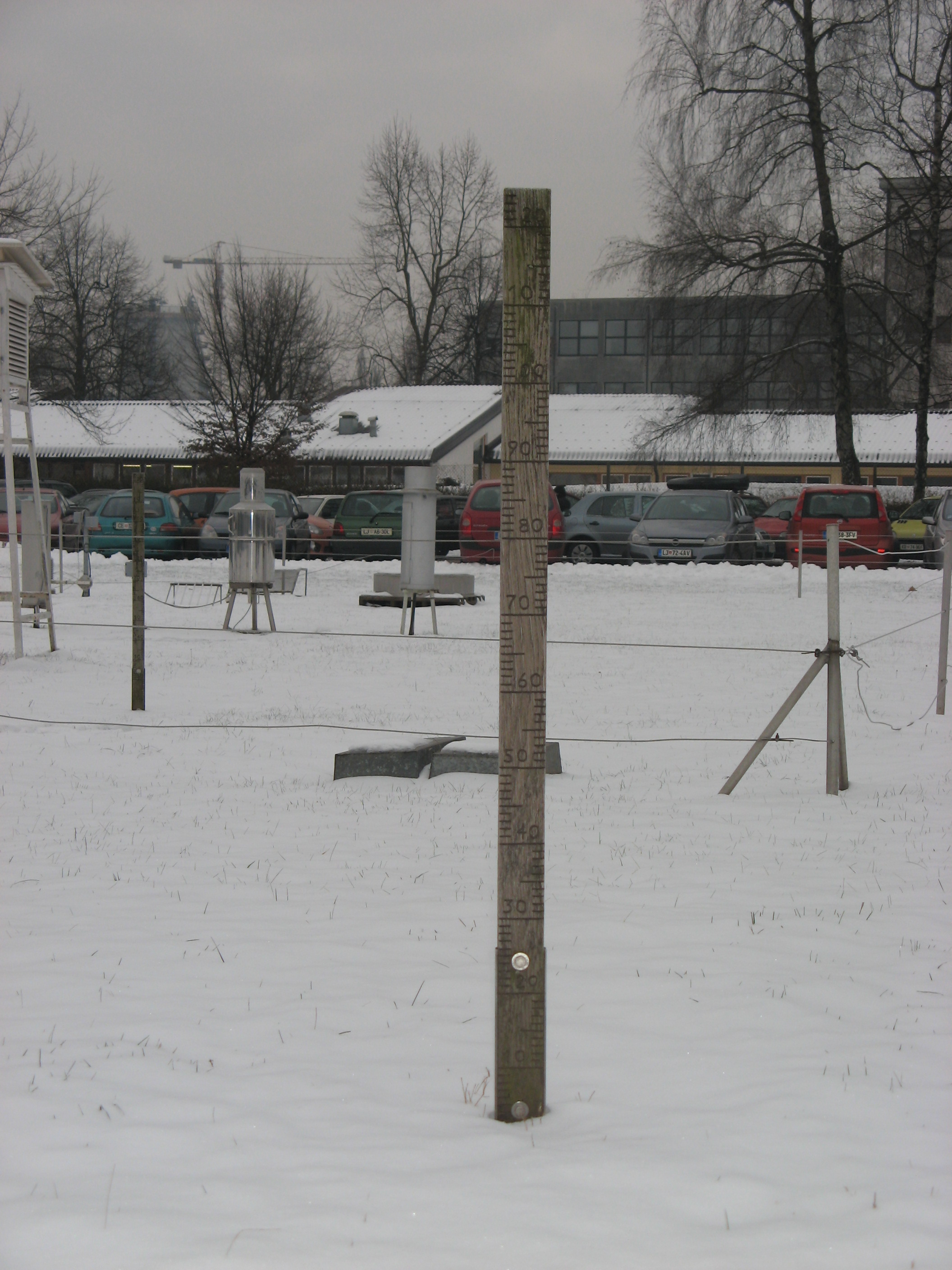 Ruler for snow depth measurements |
| SUNSHINE DURATION Sunshine duaration is measured with heliograph. Heliograph ball lens collects the sun beams in focus where trace is burnt on register tape. Register tape shows when and how long the sun shine in a single day. |
 Heliograph |
Note:
CET (Central European Time) = UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) + 1h
All the measurements at observing times refers to CET, therefore an hour must be added to the local time when daylight saving time is in use.
Source: Rakovec J.,Vrhovec T.: Osnove meteorologije za naravoslovce in tehnike